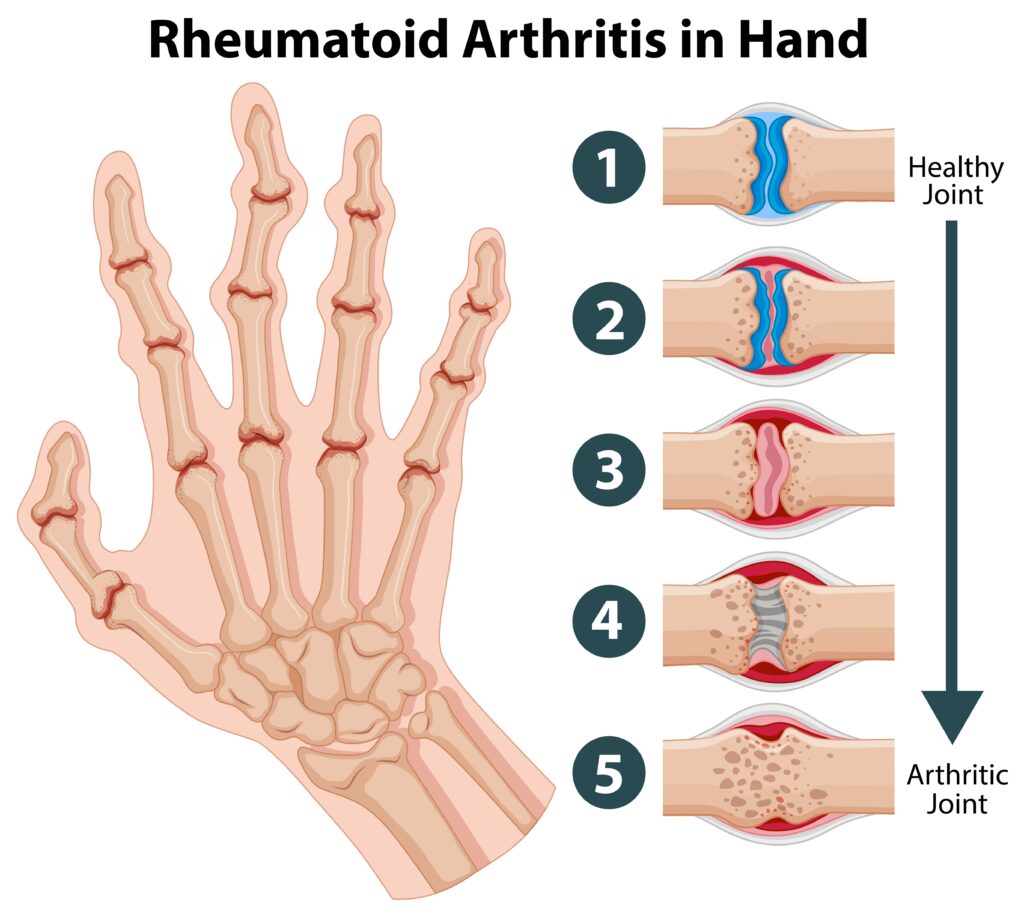
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune and systemic disease which results in chronic inflammation and destruction of synovial joints,bones.RA can affect a person’s whole system including organs such as lungs,heart,eyes.In RA,your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body resulting in inflammation,pain and swelling in the affected body parts.
Patients with RA have 20% higher risk of heart failure than the general population.
Autoimmune diseases like lupus and Rheumatoid Arthritis may also trigger Peripheral neuropathy(It happens when the nerves that transmit signals between your brain and the spinal cord to the rest of your body are damaged).
What causes RA?
The exact cause is unknown but it involves genetic factors like HLA-DRB1 gene.
SYMPTOMS
- Pain, swelling, and redness around the joints.
- When you get up in the morning or while sitting for a while, you may feel stiffness in your joints.
- Fatigue
- Anemia
- Dry Eyes
- Dry Mouth
- Numbness and tingling in hands and feet.
- Inflammation is typically involved in PIP, MCP, and wrist joints.
- Depression
- High temperature and sweating
- Poor Appetite
- The same joints on both sides of the body are usually affected.
- Chest pain and lung inflammation.
DIAGNOSIS
- blood test—RA factor positive in 70% of cases.
- Radiographs may show osteopenia and narrowing of joint space.
- Physiotherapy Management for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Physiotherapy helps in improving joint mobility, improving range of motion, and reducing pain and inflammation. Some common exercises, such as flexion, extension, and rotation movements, are performed to maintain mobility of the joints.
- Conventional physiotherapy, such as hot fomentation (hot pack) or cryotherapy (cold therapy), TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), and IFT (interferential therapy), can help in pain management.
- Some resistance band exercises help to strengthen the muscles around the affected joints and mobilization,which improves joint mobility and range of motion.
- Neuro rehabilitation exercises improve balance and coordination, which reduces the risk of falls and escape from injuries.
- Physiotherapy can help manage fatigue, a common symptom of RA, by educating and providing them different exercise plans, such as low-impact aerobic exercises, such as cycling and swimming, which can improve heart health.
- Physiotherapy helps reduce depression and anxiety by teaching patients some relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises and meditation.
Advanced Physiotherapy Techniques :
Manual Therapy—It helps in reducing pain and stiffness, improves joint mobility, breaks adhesions (taut bands, knots, or trigger points; scar tissues), reduces inflammation, and promotes healing of injured muscles.
Myofascial Release
It reduces pain and stiffness in the muscles and joints by releasing tension in the fascia and muscle, improves blood circulation, improves lymphatic drainage, reduces muscle spasm, reduces stress and anxiety, promotes healing, and provides good sleeping habits.
IASTM
Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) is a manual therapy technique that uses metallic tools with different shapes to mobilize and release tension in the soft tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, and tendons. This therapy helps in improving blood circulation by releasing the muscle and reducing pain, stiffness, and spasm simultaneously.
Dry Needling
Dry needling is a technique in which we put tiny needles to target specific trigger points. It helps to reduce pain, swelling, and stiffness, to improve blood flow, to improve movement of joints, etc.
Kinesiology Taping
Kinesiology Taping (Kinesio = Movement) is a stretchy tape that is used to support the muscle in order to facilitate (or initiate) the action of that muscle. If the muscle is overactive, this taping technique helps in inhibiting the action of that muscle.
It helps to reduce edema/swelling by improving lymphatic drainage. It helps to correct the deformity (inappropriate alignment of the bones and other structures).